Cao, H., et al. A Comparative Study on Immune Protection Efficacy: An HSV-1 Trivalent Antigen Subunit Vaccine Formulated with a Cellular Immunity-Inducing Adjuvant Versus an mRNA Vaccine. Vaccines (Basel), 2025 Sep 10, 13(9):958.
Cao, H., et al. A Comparative Study on Immune Protection Efficacy: An HSV-1 Trivalent Antigen Subunit Vaccine Formulated with a Cellular Immunity-Inducing Adjuvant Versus an mRNA Vaccine. Vaccines (Basel), 2025 Sep 10, 13(9):958. PMID: 41012161
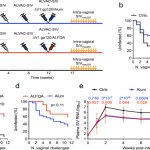
- The study compares the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of two different vaccine platforms against HSV-1 infection: an mRNA vaccine and a subunit vaccine formulated with adjuvants (CpG ODNs and QS-21).
- Both mRNA and subunit vaccines targeting gC1, gD1, and gE1 antigens induced robust protective immunity against acute HSV-1 infection in mice. The vaccines significantly reduced viral loads in tissues, especially in neural tissues like the trigeminal nerve and spinal cord, with the adjuvanted subunit vaccine showing slightly superior neuroprotective efficacy in some tissues.
- The subunit vaccine formulated with adjuvants CpG and QS-21 elicited higher gE1-specific IgG titers compared to the mRNA vaccine and induced cellular immune responses comparable to the mRNA vaccine, primarily stimulating CD4+ T cells that produce IL-2 and IFN-γ. Both vaccine platforms caused minimal neural damage and controlled neural viral dissemination.
- Viral loads in tissues such as the brain and spinal cord were markedly lower in vaccinated mice, with the subunit vaccine showing particularly strong neuroprotective effects, including reduced viral presence in the trigeminal nerve. The vaccine-induced immune responses correlated with the neutralizing antibody titers and cellular immunity markers.
- The study highlights the potential of these vaccines, especially the subunit formulation with CpG and QS-21, as practical and effective prophylactics against HSV-1, with advantages such as stability and ease of storage, warranting further research for long-term protection and clinical application.
Click here to access the full scientific paper.
Recent Posts