Ye, L., et al. Effects of immune response on different nano-adjuvants combined with H11 antigen of Haemonchus contortus.
Int Immunopharmacol, 2024 Dec 25, 143(Pt 3):113602. PMID: 39536488.
The study indicates that nano-adjuvants offer a promising alternative to traditional adjuvants for inducing robust and lasting immune responses, particularly in the context of developing vaccines against parasitic infections like Haemonchus contortus.
The effects of nano-adjuvants such as immunostimulating complex matrix (IMX), lipid nanoparticles (LNP), and AddaS03™ differed from traditional adjuvants like QuilA (unformulated). Unlike traditional adjuvants, nano-adjuvants can slow the release of antigens, prolonging the time immune cells have to recognize these antigens, thereby improving the overall immune response. This is particularly important for sustaining long-term immunity. Nano-adjuvants tend to facilitate more complex immune mechanisms, including both cell-mediated (Th1 and Th17 responses) and humoral immune responses, whereas traditional adjuvants like QuilA are more focused on stimulating humoral immunity.
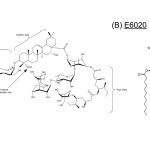
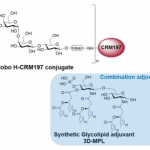
Comments from Desert King: This paper emphasizes the importance of formulations and particulate adjuvants to improve immunogenicity, which we fully agree with. However, the authors did not select a proper “traditional” adjuvant or use an appropriate QS-21 formulation for the study. QuilA, although not suitable for human vaccines, is a potent adjuvant. This paper demonstrates that the QuilA-adjuvanted vaccine induced the highest IgM and IgG responses, the highest IFN-γ cytokine levels, and strong lymphocyte proliferation similar to the nano-adjuvants. QS-21 is one of the most effective adjuvants when properly formulated. QS-21-based nanoparticle adjuvants (e.g., AS01b, Matrix-M, ALFQ, etc.) are proven to be extremely potent formulations and are being tested in multiple clinical trials and approved human vaccine.
Click here to access the full scientific paper.