Pirahmadi S. et. al.: Selection of combination adjuvants for enhanced immunogenicity of a recombinant CelTOS vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2025 Jan 9, 748:151310. PMID: 39809136.
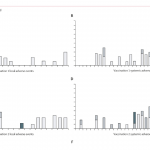
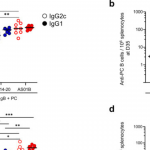
In the current study, the immunogenicity of Plasmodium falciparum cell traversal protein for ookinetes and sporozoites (PfCelTOS) were intended to improve by three different adjuvants: MPL, Poly I:C, and QS-21 alone or a dual mixture (Poly I:C/QS-21; PQ), or a triple mixture (MPL/Poly I:C/QS-21; MPQ) in BALB/c mice with a prime-boost(2) immunization schedule.
PQ and MPQ induced the strongest secretion of IFN-γ and TNF cytokines in splenocytes, but there was no significant difference in IL-10 levels compared to other groups. All adjuvants increased the total IgG levels. The highest titers and avidity antibodies for total IgG, and IgG2a and IgG2b isotypes were induced by PQ and MPQ. The functional transmission-blocking activity (TRA) of anti-PfCelTOS antibodies using a mosquito-feeding assay determined that PQ and MPQ had significantly the highest ability to inhibit oocyst development in Anopheles stephensi. The study suggests that antibodies with high avidity, as induced by the combination of adjuvants with PfCelTOS, play a vital role in inhibiting the development of malaria parasites in mosquitoes, thereby contributing to the reduction of malaria transmission.
The study demonstrates that administering the PfCelTOS antigen with combination adjuvants significantly enhances immune responses compared to using the antigen alone or with single adjuvants. This further proves the potential superiority of combination adjuvant strategies in vaccine development. Interestingly, however, the dual PQ combination induced immune responses and functional activity comparable to those achieved with the triple MPQ adjuvant, suggesting that the dual adjuvant combination could provide a highly effective formulation while having important implications for cost and safety by minimizing the number of adjuvants needed.
Click here to access the full scientific paper.