Song, Y., et al. 50-Fold Adjuvant and 20-Fold Antigen Vaccine Dose Sparing from Nanoliposome Display of a Stabilized Malarial Protein Antigen.
Song, Y., et al. 50-Fold Adjuvant and 20-Fold Antigen Vaccine Dose Sparing from Nanoliposome Display of a Stabilized Malarial Protein Antigen.
CS Nano, 2025 Mar 18, 19(10):10103-10112. PMID: 40099532
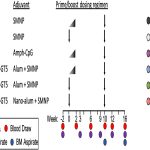
- The study investigates the use of nanoliposomes to enhance the immunogenicity of a stabilized malarial protein antigen, Pfs48/45, focusing on antigen and adjuvant dose sparing.
- While both MPLA and QS-21 contributed positively to the vaccine’s performance, the effectiveness of the complete formulation with both immune modulators combined in the liposomal formulation, along with the cobalt porphyrin phospholipid (CoPoP), was emphasized as the best in terms of eliciting a robust immune response with substantial dose-sparing advantages. By displaying the antigen on CoPoP liposomes, the research demonstrated a significant 50-fold reduction in the required adjuvant doses and a 20-fold reduction in the antigen doses while still eliciting strong antibody responses in mice. This liposome-bound format allowed for superior antibody titers compared to soluble forms, supporting the potential of this approach for the development of more effective and cost-efficient malaria vaccines.
- The results emphasize the importance of nanoparticle-based vaccine strategies in improving immunogenicity and enabling scalable production for future vaccine deployment.
Click here to access the full scientific paper.
Recent Posts