Scaria, P.V., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) Protein-Protein Conjugate Induces Similar or Better Antibody Responses as Spike mRNA in Rhesus Macaques. Vaccines (Basel), 2025 Jun 17, 13(6):648.
Scaria, P.V., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) Protein-Protein Conjugate Induces Similar or Better Antibody Responses as Spike mRNA in Rhesus Macaques. Vaccines (Basel), 2025 Jun 17, 13(6):648. PMID: 40573979
- This study demonstrates that an RBD-EcoCRM conjugate vaccine adjuvanted with AS01 can induce robust, high-quality antibody responses in rhesus macaques that are comparable or superior to those elicited by the approved mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2).
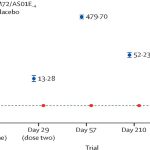
- The conjugate vaccine elicited strong binding, neutralizing, and inhibiting antibodies against the virus and its variants, with immune responses persisting for at least six months post-vaccination. The conjugate vaccine with AS01 adjuvant produced higher or similar levels of serum antibodies, virus neutralization activity, and binding inhibition against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Additionally, the conjugate vaccine elicited antibody responses against both the RBD and full-length Spike proteins, with some indications of broader epitope recognition, which might contribute to its efficacy.
- One notable aspect is the durability of the immune response; the antibody levels and neutralization activity, although waning over time, remained higher or comparable in the conjugate group relative to the mRNA group at later time points, such as 6 months post-vaccination. Furthermore, the subclass profile of antibodies induced by the conjugate vaccine (more IgG2 and IgG4 over time) and the natural waning of antibody levels may influence the long-term protection differently.
- Importantly, the potential advantages include better safety profiles, easier manufacturing, stability, and adaptability to viral evolution, making the AS01b-adjuvanted conjugate vaccine a promising alternative, especially in settings where mRNA vaccines might pose logistical challenges or have safety concerns. The conjugate vaccines are effective, scalable, and possibly more accessible alternatives for COVID-19 immunization, especially in low- and middle-income settings. However, direct head-to-head comparative efficacy data in humans would be necessary for definitive conclusions.
Click here to access the full scientific paper.
Recent Posts